This text was developed with the assistance of artificial intelligence.
The History of Morse Code: Connecting the World Through Dots and Dashes
The Birth of Morse Code:
In the early 19th century, two remarkable individuals, Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail, joined forces in a collaborative effort that would change the course of communication history. Samuel Morse, a multifaceted American artist and inventor, possessed a vision of bridging vast distances through innovative means. Alfred Vail, a highly skilled mechanic, shared Morse’s enthusiasm for advancing the field of telecommunications.
Their ambitious undertaking began with a singular objective in mind: to develop a revolutionary method of communication that could transmit messages with remarkable speed and efficiency over extended distances. Morse and Vail were acutely aware of the limitations of existing communication systems, which often resulted in slow and unreliable transmission of information.
In 1838, Samuel Morse unveiled their groundbreaking invention to the world for the very first time. This pivotal moment marked the public debut of the Morse code system, a creation born out of their relentless dedication and ingenuity. Morse’s demonstration not only showcased the system’s practicality but also highlighted its immense potential to transform long-distance communication, setting the stage for the technological revolution that would follow.
The Morse code system, consisting of dots and dashes representing letters and numbers, became a fundamental building block in the evolution of telecommunications. Its enduring legacy can still be felt in the modern world, as it laid the foundation for the rapid exchange of information and the interconnected global society we know today. Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail’s visionary collaboration forever changed the way humanity communicates, proving that innovation and determination can transcend the boundaries of time and distance.

The Telegraph Revolution:
Morse code found its most significant application in the telegraph, which was the first electrical telecommunications system. The first telegraph line, running from Washington, D.C., to Baltimore, Maryland, was completed in 1844. It marked the beginning of a new era in communication. Messages that once took days or weeks to travel could now be transmitted in a matter of minutes.
The Dots and Dashes:
Morse code relies on a combination of dots and dashes to represent letters and numbers. The code is characterized by a series of short signals (dots) and long signals (dashes), which are used to form characters. Each letter and number has a unique code, making it a highly efficient means of communication.
The Global Reach:
Morse code quickly spread around the world, connecting continents and enabling swift communication between countries. Its impact on various industries, such as shipping, aviation, and the military, cannot be overstated. Ships at sea, for example, relied on Morse code to send distress signals, enabling timely rescue operations.
Morse Code in Warfare:
During times of conflict, Morse code played a crucial role in military communication. Soldiers and field agents used Morse code to transmit orders, intelligence, and vital information. It provided a secure and efficient means of conveying sensitive messages.
The Advent of Radio:
With the emergence of radio technology in the early 20th century, Morse code found a new home in the world of wireless communication. Radio operators around the globe used Morse code to establish contact and exchange messages, helping to foster international collaboration and information exchange.
The Enduring Legacy:
Although modern telecommunications have largely moved beyond Morse code, its legacy endures. Amateur radio operators, also known as “hams,” still use Morse code as part of their hobby. Additionally, Morse code is a valuable skill for emergency situations when other forms of communication may fail.
In conclusion, Morse code represents a pivotal moment in the history of telecommunications. Its invention and adoption transformed the way people communicated, bridging great distances and connecting the world in ways previously unimaginable. While no longer the primary method of communication, Morse code remains a symbol of innovation and the power of human ingenuity.
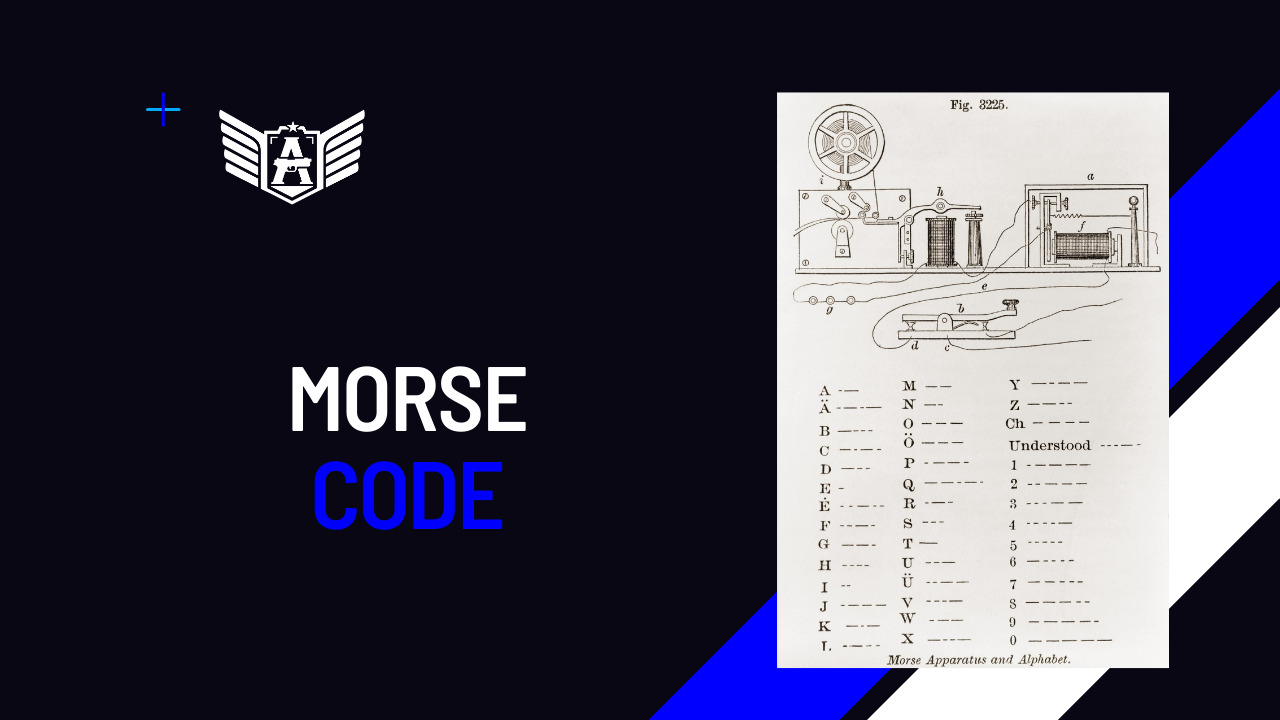
The code
A: .-
B: -…
C: -.-.
D: -..
E: .
F: ..-.
G: –.
H: ….
I: ..
J: .—
K: -.-
L: .-..
M: —
N: -.
O: —
P: .–.
Q: –.-
R: .-.
S: …
T: –
U: ..-
V: …-
W: .–
X: -..-
Y: -.–
Z: –..
0: —–
1: .—-
2: ..—
3: …–
4: ….-
5: …..
6: -….
7: –…
8: —..
9: —-.
Each letter is represented by a series of dots (.) and dashes (-), with spaces or short pauses between each letter and longer pauses between each word. This code allowed for efficient communication using telegraphy and is still recognized and used by enthusiasts today.
Too hard? Try this translator:
https://morsecode.world/international/translator.html