ATTENTION: This study appears to have significant technical limitations that are not the responsibility of ABA Intl. ABA Intl merely reproduces the authors’ publication without making any value judgments of any kind. Please use it with responsibility and professional skepticism.
Pradip Saini, Prof. T. Onima Reddy, and Prof. Vikram Singh from the Department of Physical Education, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India, published an article titled ‘Influence of Dry Fire Practice on Rifle Shooting Performance of School-Going Students’ in the International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology in 2023. The article aims to investigate the impact of dry fire practice on the rifle shooting performance of 30 students aged between 14 and 16 years.
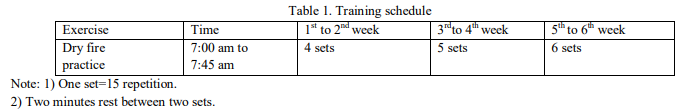
In this study, 30 school-going male students aged 14 to 16 were randomly selected from Dr. Nandurkavidyalaya, Yavatmal, Maharashtra, representing diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. The criterion measure involved assessing the rifle shooting performance of these students using a .22 Long rifle shooting test, recorded by the rifle shooting target board. The test was administered both before and after a six-week dry fire practice training program. The shooting test involved students standing 10 meters from a target board and making 40 shots, with different points awarded based on shot accuracy. The study employed an experimental design with an experimental group (receiving the dry fire practice) and a control group (no training), involving 45-minute daily sessions for six weeks. After completing the 40 trials, individual scores were tallied for the final result.
The study aimed to assess the impact of six weeks of dry fire practice on the rifle shooting performance of secondary school students. Data was collected by conducting a .22 long rifle shooting test before and after the training program, and the collected data was analyzed using the ‘T’-test statistical technique. Notably, the pre-test and post-test scores of the experimental group demonstrated a significant difference, indicating that the dry fire practice program had a significant effect on their performance. However, there was no significant difference in the post-test scores between the experimental and control groups, suggesting that the null hypothesis was rejected. These findings highlight the positive influence of dry fire practice on the shooting performance of the experimental group.
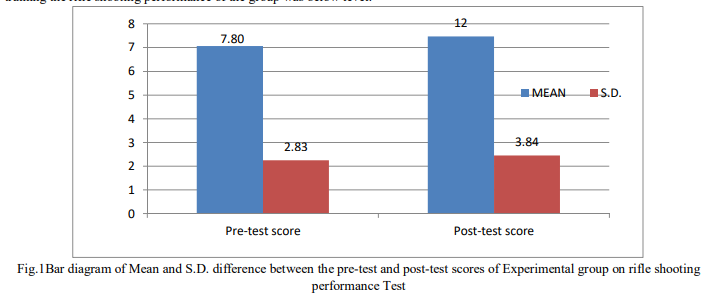
Acording to the authors:
V. CONCLUSIONS
Within the limitations of the present study, the following conclusions were drawn:
1) The study shows hat there was significance difference in dry fire practice on rifle shooting performance of the experimental and control groups.
2) It was also concluded that there were significance differences in post-test results on the experimental and control groups.3) It was also found that there were significance differences in pre-test and post-test results of rifle shooting performance of the experimental group.
4) Finally it was concluded that six-week dry fire practice program significantly effects on rifle shooting performance of secondary school students.
Saini, P., Reddy, T. O., & Singh, V. Influence of Dry Fire Practice on Rifle Shooting Performance of School Going Students.




